First, make sure nginx is built with IPv6 support
You will also need to know your IPv6 range, and what address(s) you want to use.
In this example, I have a /128 allocation of IPv6 addresses to use:
Scope:Link is the mac address of the interface, and Scope:Global is the usable range.
So, I'm going to add the 2nd address in the range to the interface:
This is now present in the ifconfig results
You then need to add the address to the server block for your site in the nginx configuration
Restart nginx
If you have the ability to from a different server, check you can ping the new IPv6 address
Then, you will need to create an AAAA DNS record for the address

ping the new address
You can then validate the IPv6 connectivity using a website such as http://ipv6-test.com/validate.php

Code:
root@debian:~# nginx -V | grep -w ipv6
nginx version: nginx/1.7.1
built by gcc 4.7.2 (Debian 4.7.2-5)
TLS SNI support enabled
configure arguments: --prefix=/etc/nginx --sbin-path=/usr/sbin/nginx --conf-path=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf --error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log --http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log --pid-path=/var/run/nginx.pid --lock-path=/var/run/nginx.lock --http-client-body-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/client_temp --http-proxy-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/proxy_temp --http-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/fastcgi_temp --http-uwsgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/uwsgi_temp --http-scgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/scgi_temp --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_realip_module --with-http_addition_module --with-http_sub_module --with-http_dav_module --with-http_flv_module --with-http_mp4_module --with-http_gunzip_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-http_random_index_module --with-http_secure_link_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_auth_request_module --with-mail --with-mail_ssl_module --with-file-aio --with-http_spdy_module --with-cc-opt='-g -O2 -fstack-protector --param=ssp-buffer-size=4 -Wformat -Werror=format-security -Wp,-D_FORTIFY_SOURCE=2' --with-ld-opt='-Wl,-z,relro -Wl,--as-needed' --with-ipv6You will also need to know your IPv6 range, and what address(s) you want to use.
In this example, I have a /128 allocation of IPv6 addresses to use:
Code:
inet6 addr: fe80::4e72:b9ff:fe7b:b275/64 Scope:Link
inet6 addr: 2001:41d0:8:c463::1/128 Scope:GlobalSo, I'm going to add the 2nd address in the range to the interface:
Code:
/sbin/ip -6 addr add 2001:41d0:8:c463::2/128 dev eth0This is now present in the ifconfig results
Code:
root@debian:~# ifconfig
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 4c:72:b9:7b:b2:75
inet addr:5.135.187.99 Bcast:5.135.187.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::4e72:b9ff:fe7b:b275/64 Scope:Link
inet6 addr: 2001:41d0:8:c463::2/128 Scope:Global
inet6 addr: 2001:41d0:8:c463::1/128 Scope:GlobalYou then need to add the address to the server block for your site in the nginx configuration
Code:
server {
listen 5.135.187.99:80;
listen [2001:41d0:8:c463::2]:80;
server_name test.mattwservices.co.uk;Restart nginx
Code:
service nginx restartIf you have the ability to from a different server, check you can ping the new IPv6 address
Code:
root@ny1:~# ping6 2001:41d0:8:c463::2
PING 2001:41d0:8:c463::2(2001:41d0:8:c463::2) 56 data bytes
64 bytes from 2001:41d0:8:c463::2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=53 time=1022 ms
64 bytes from 2001:41d0:8:c463::2: icmp_seq=2 ttl=53 time=79.9 ms
64 bytes from 2001:41d0:8:c463::2: icmp_seq=3 ttl=53 time=79.9 ms
64 bytes from 2001:41d0:8:c463::2: icmp_seq=4 ttl=53 time=79.9 ms
64 bytes from 2001:41d0:8:c463::2: icmp_seq=5 ttl=53 time=79.9 msThen, you will need to create an AAAA DNS record for the address
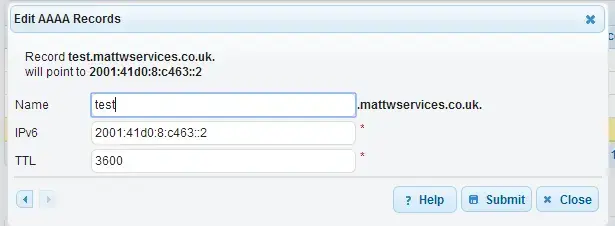
ping the new address
Code:
root@ny1:/etc/nginx/conf.d# ping6 test.mattwservices.co.uk
PING test.mattwservices.co.uk(2001:41d0:8:c463::2) 56 data bytes
64 bytes from 2001:41d0:8:c463::2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=53 time=79.8 ms
64 bytes from 2001:41d0:8:c463::2: icmp_seq=2 ttl=53 time=79.9 ms
64 bytes from 2001:41d0:8:c463::2: icmp_seq=3 ttl=53 time=80.0 ms